Intro
In the realm of business operations, sales and marketing strategies are intertwined forces driving customer acquisition and revenue generation. While marketing efforts focus on building awareness and nurturing potential leads, sales strategies entail direct interactions with customers to close deals and foster relationships.
Note: 🍋 Throughout this guide we will use the example of a food supplement company to better illustrate each task and information.
What is a Sales Strategy?
Your sales and marketing strategies are very closely related. While marketing focuses on generating and nurturing a pipeline of potential customers, sales is more focused on the direct interaction with the customer and the sales team and the process of closing deals with individual customers,
Depending on the type of product or service you are offering, sales activities that include the direct interaction with individual customers, become more or less important. Generally speaking the more complex your product the more focus and resources you will have to put into your sales activities.
For example, businesses that sell SaaS, consulting services or insurance will need to spend more time on explaining their product and convincing individual clients than businesses that sell clothes via an online shop or food supplements via amazon. The latter will probably put more resources into creating awareness and educating their audience through marketing activities.
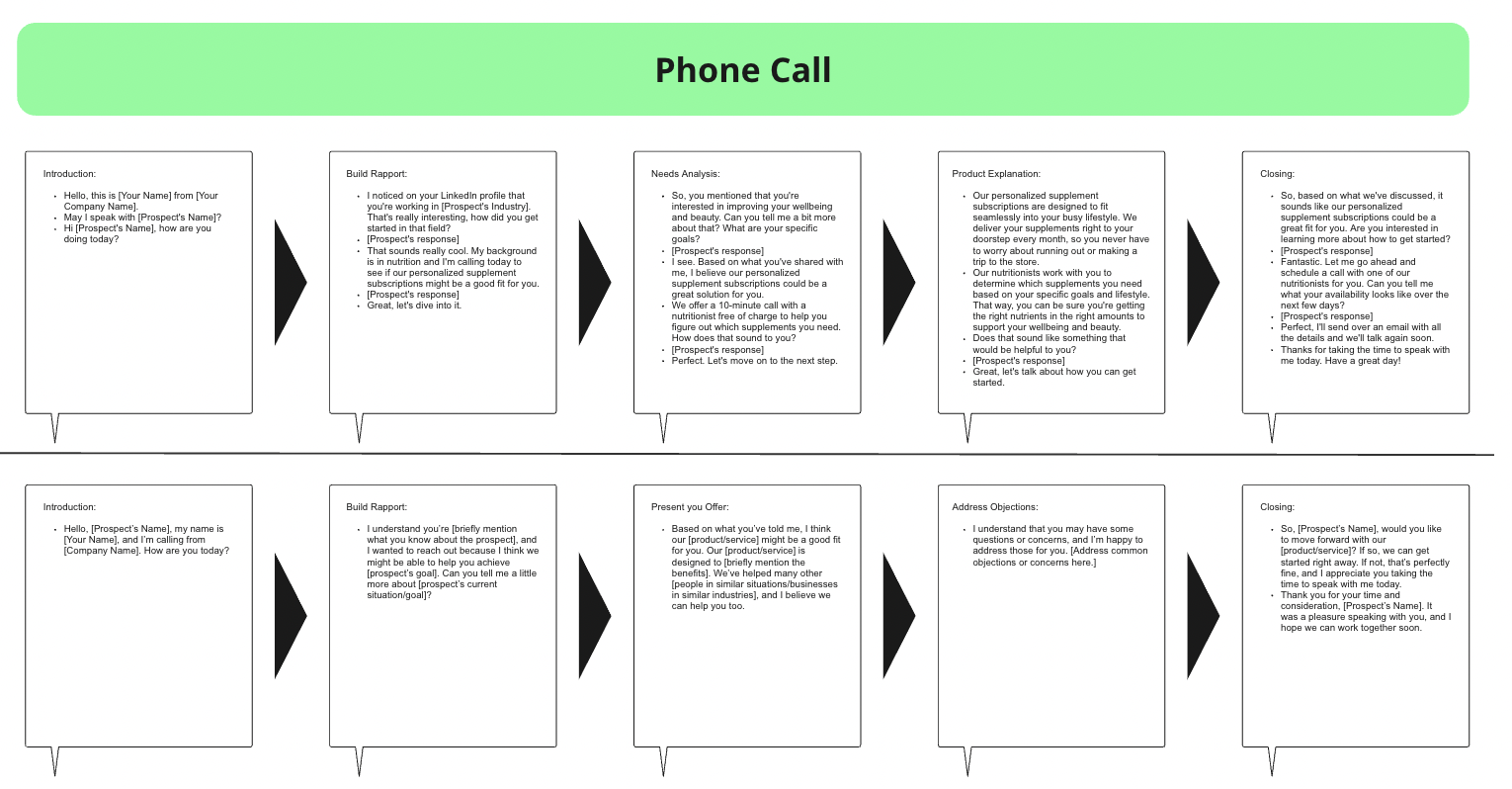
Traditionally when you hear the word sales, you probably think of the nice shop clerk at your favorite retail store trying to convince you to buy that overpriced day cream that makes you look 10 years younger or the sales people traveling the whole country in their VW passat visiting client after client to “close the deal”. However, in this toolkit we will rather focus on more modern, mostly digital sales approaches suitable for new businesses in the digital age.
What are the Benefits of a well defined Sales Strategy?
In today’s dynamic business landscape, a well-defined sales strategy is indispensable for all types of businesses, serving as a roadmap for customer interactions that drives revenue growth and cultivates enduring client relationships.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: A well-defined sales strategy enables businesses to deeply engage with customers at every touchpoint, fostering meaningful interactions that build trust and loyalty over time.
- Streamlined Sales Process: It allows businesses to optimize and streamline their sales processes, eliminating inefficiencies and redundancies to ensure a smoother and more efficient journey from lead generation to conversion.
- Increased Revenue Generation: By implementing a structured approach to sales, businesses can maximize revenue generation opportunities, capitalize on cross-selling and upselling opportunities, and drive sustainable growth over the long term.
- Improved Customer Retention: A robust sales strategy focuses not only on acquiring new customers but also on nurturing existing relationships, leading to higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention rates.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Utilizing data analytics and insights, a well-defined sales strategy empowers businesses to make informed decisions, identify trends, and adapt strategies in real-time, driving continuous improvement and agility in the marketplace.
A well defined sales strategy is crucial for all types of businesses
- For Entrepreneurs, a well-defined sales strategy offers a systematic approach to acquiring customers and scaling their business operations efficiently, laying the groundwork for sustained growth and success.
- For Start-Ups, it provides a framework for navigating the complexities of the sales process, ensuring effective customer acquisition and sustainable growth, even in the face of limited resources and competition.
- For Corporates, a robust sales strategy facilitates consistent revenue generation and strengthens customer relationships, contributing to long-term profitability and market dominance in an ever-evolving business landscape.
- For Investors, a well-defined sales strategy demonstrates a company’s ability to drive revenue growth and maximize return on investment, making it an essential factor in investment decisions and signaling the potential for long-term value creation.



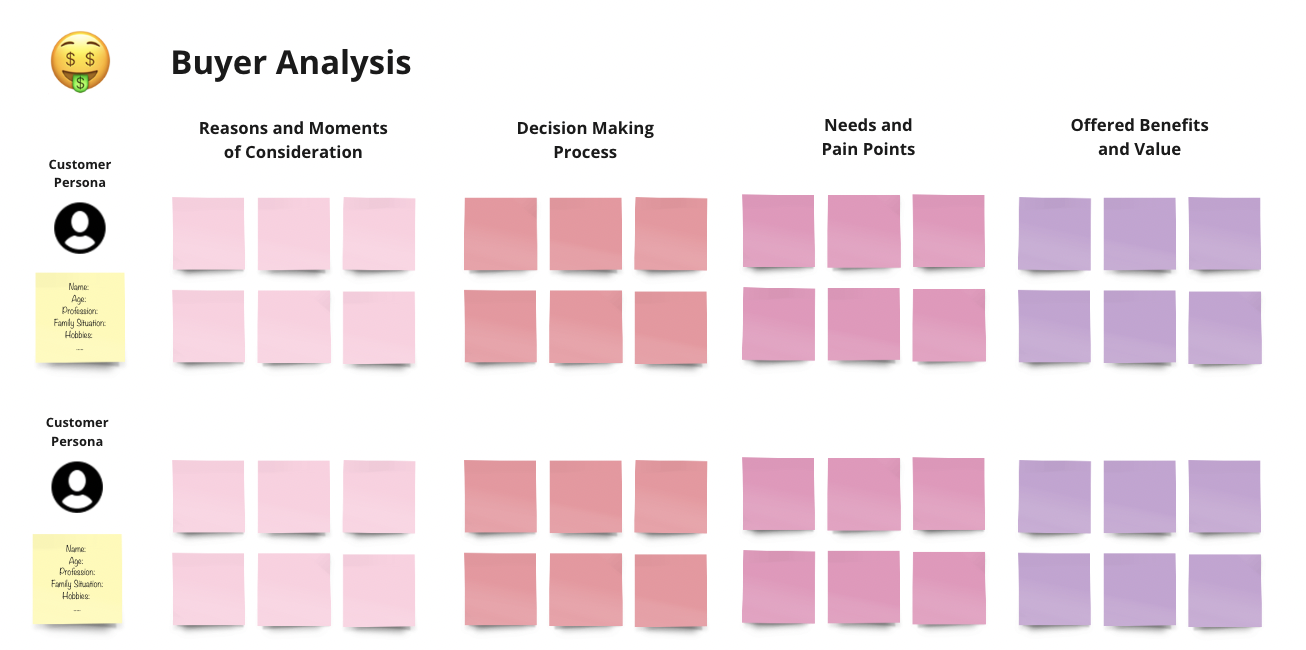

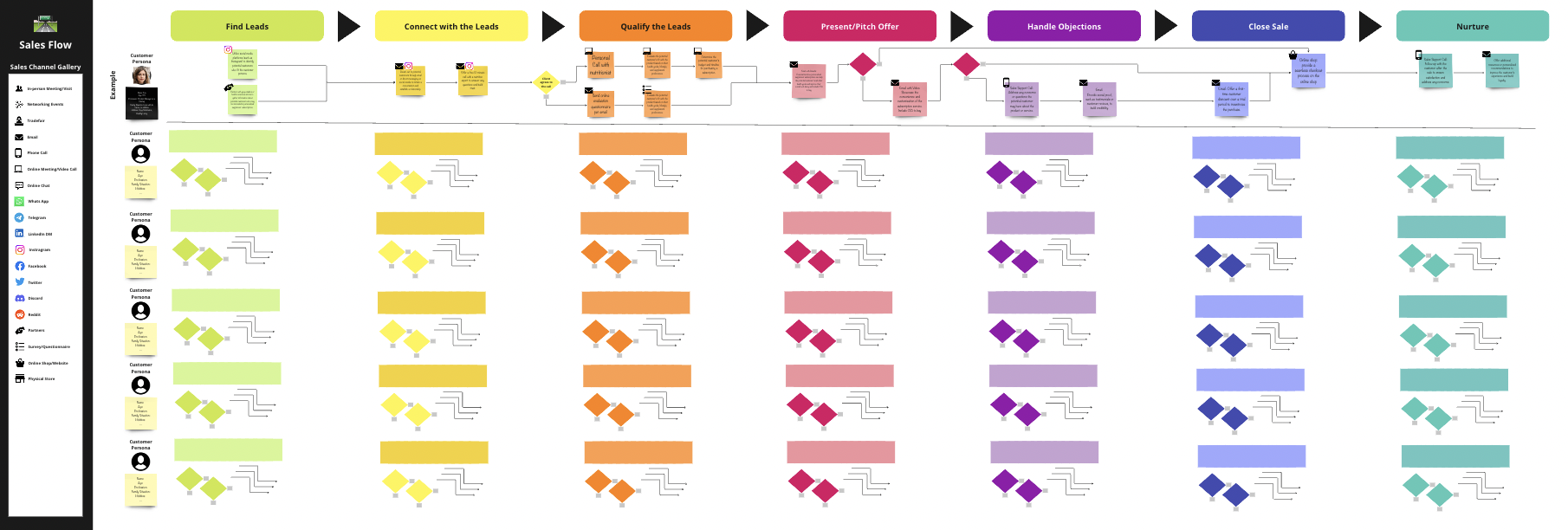

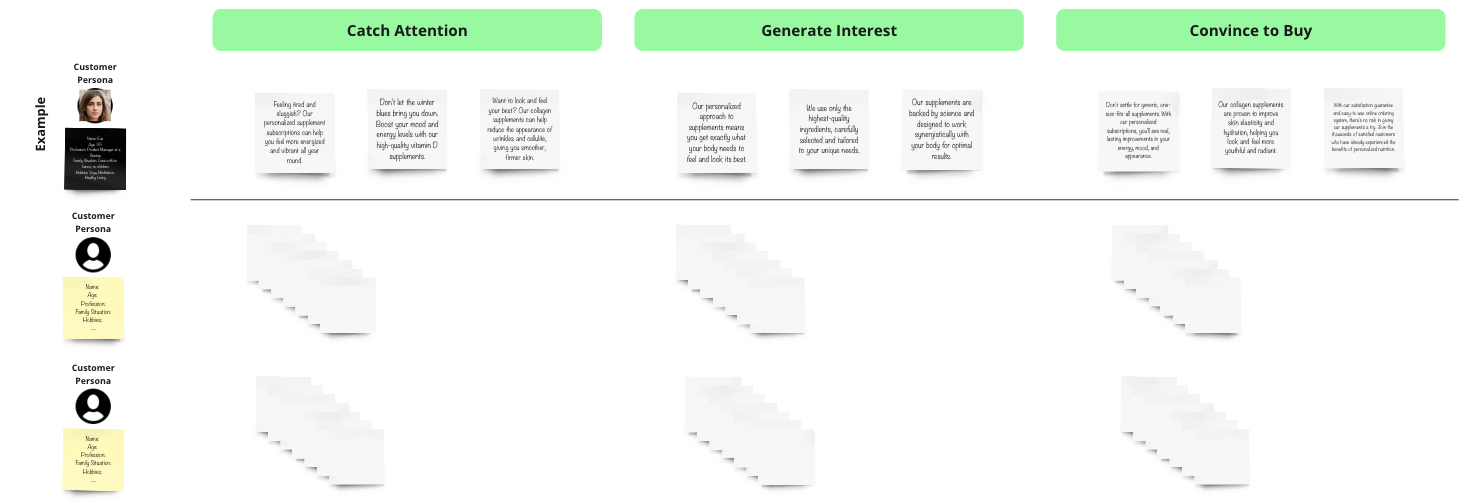


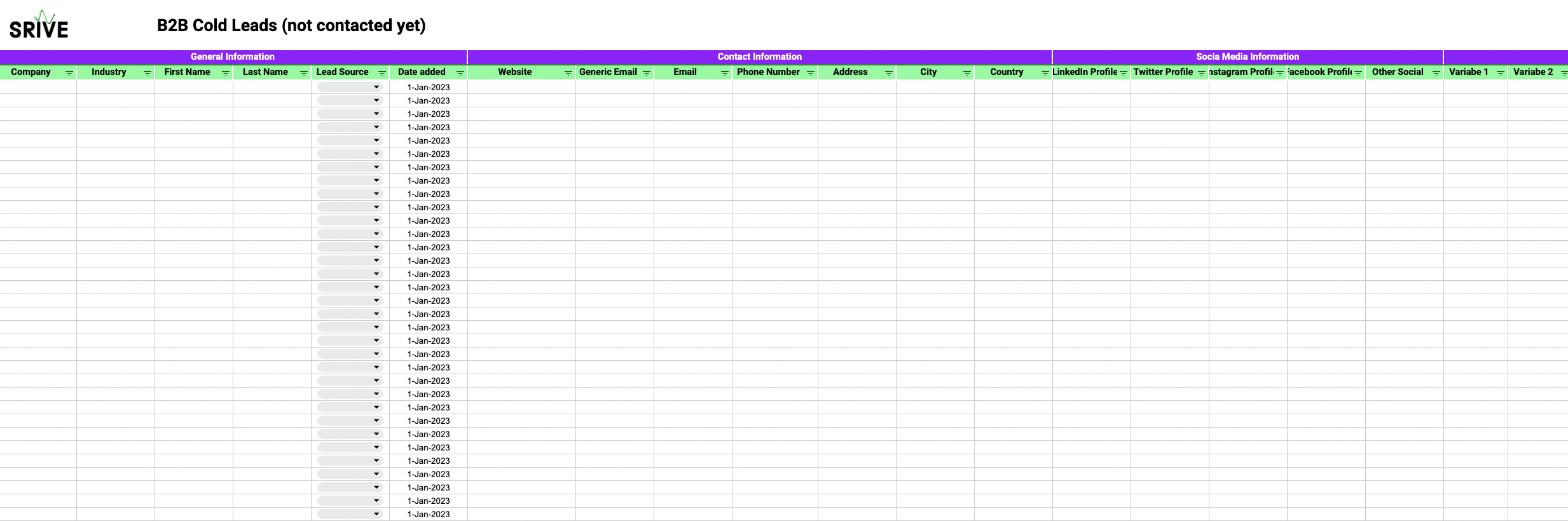



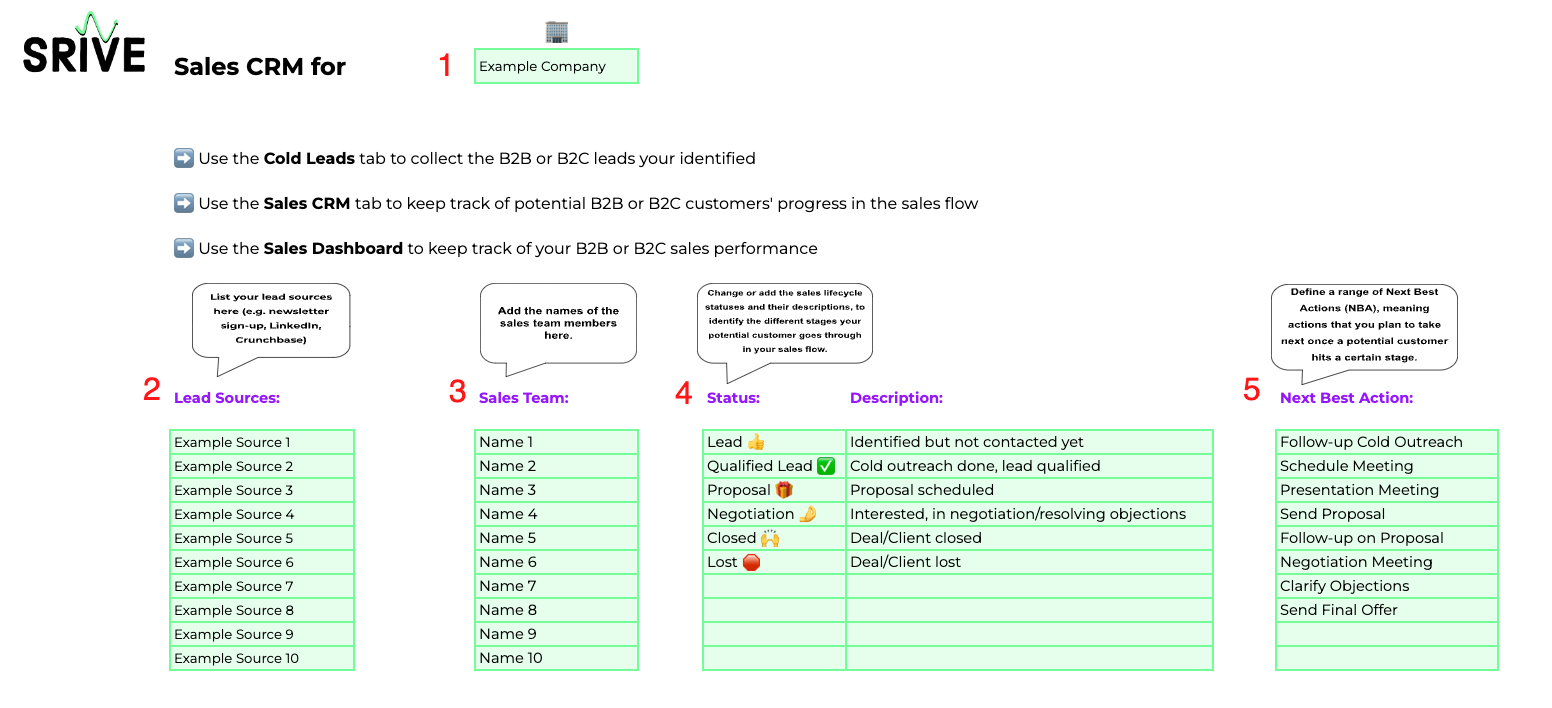
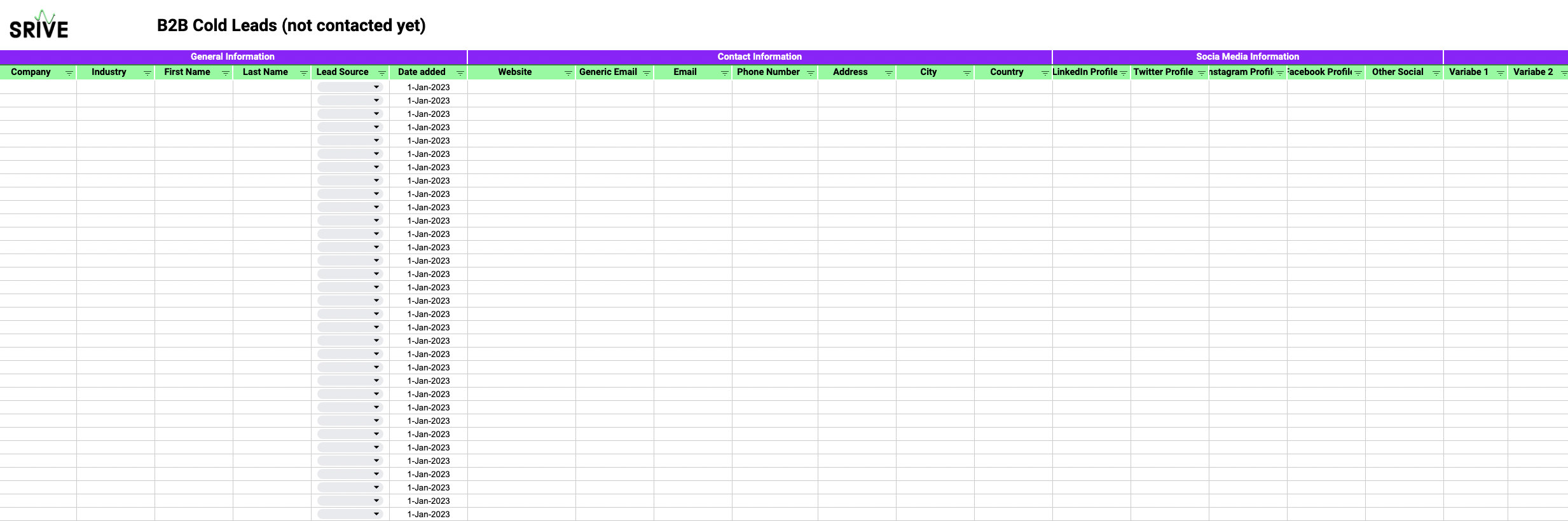
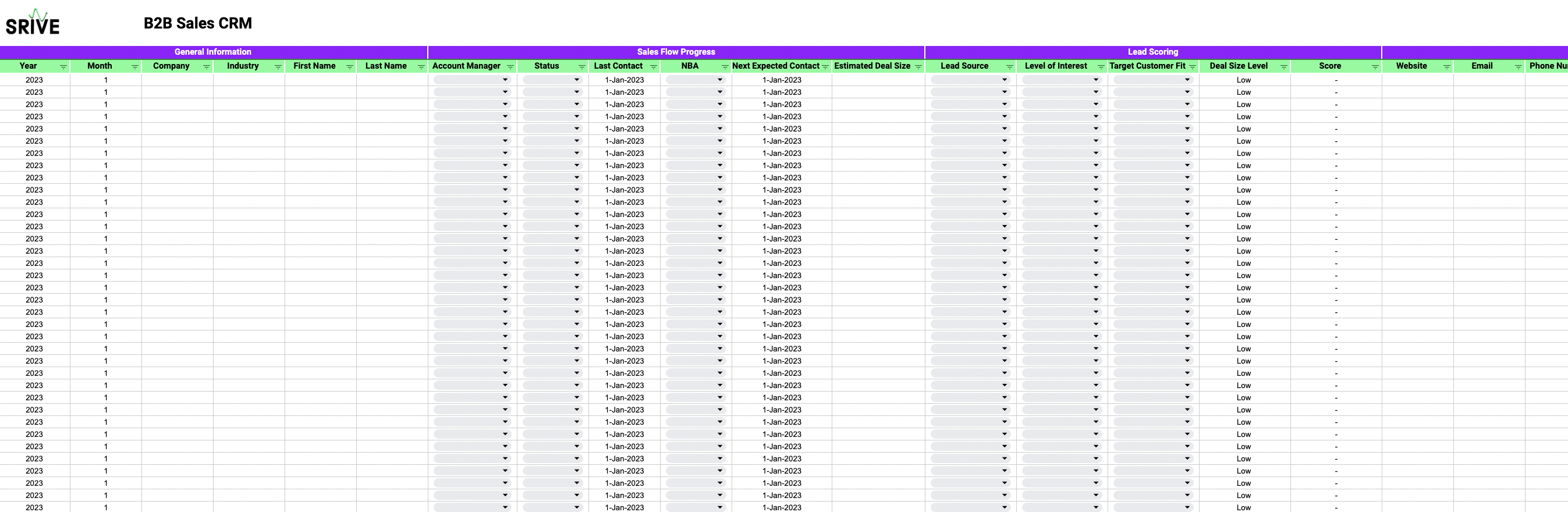
 Lead Source: Is the potential client an inbound lead, meaning they proactively showed interest in your business e.g. through filling out a contact form or signing up for a newsletter. Or is there a lead you reached out to first? ➡️ Inbound leads may be more valuable since they actively showed interest.
Lead Source: Is the potential client an inbound lead, meaning they proactively showed interest in your business e.g. through filling out a contact form or signing up for a newsletter. Or is there a lead you reached out to first? ➡️ Inbound leads may be more valuable since they actively showed interest.